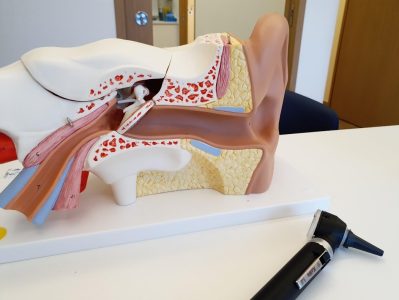
The Eustachian tube is a narrow passage-way connecting the middle ear to the back of the nose. When the Eustachian tube is blocked or is unable to help equalize pressure in the middle ear, patients complain of pain in their affected ear, a constant feeling of fullness, or tinnitus (extra auditory sounds ) in their ear. Eustachian tube dysfunction can resolve spontaneously in a day or two but if it does not, it is imperative to consult an ENT doctor.
There are different types of Eustachian tube disorders which an ENT doctor must evaluate and diagnose you with:
- Patulous ETD: this occurs when the cartilaginous portion of the eustachian tube is wide open resulting in a blocked ear sensation which improves when the head is in a dependent position.
- Obstructive ETD: this occurs when the eustachian tube does not open up as quickly or as optimally as it is supposed to, resulting in fluid accumulating in the middle ear that causes muffled hearing, pain or ear pressure. Additionally, nasopharyngeal cancer can sometimes present in this manner hence a nasoendoscopic examination is warranted to rule out malignancy. Patients with poorly controlled allergic rhinitis , nasal polyps or sinsusitis can also experience obstructive ETD.
- Baro challenge induced ETD: this is similar to obstructive ETD in response to altitude changes or atmospheric depth changes.
What are the symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction?
- Blocked ear sensation
- Ear fullness
- Echoey quality of their voice
- Tinnitus
- Ear pain and discomfort
TREATMENT
Eustachian tube disorders can be alleviated by these simple self-measures:
- Chewing gum
- Yawning
- Swallowing
- Using a saline spray to clear the nasal passageways
- Using the Valsalva method (forcibly blowing out through your mouth while keeping the nostrils and mouth closed)
If these measures do not work for you, medical consultation will be needed to identify the problem and receive the right treatment. Treatment can range from managing nasal conditions and infections to surgical procedures such as:
- Eustachian tuboplasty: expansion of the eustachian tube using a tiny medical balloon
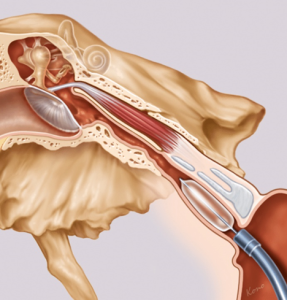
- Myringotomy and grommet tube insertion: to help reduce middle ear pressures and allow middle ear ventilation