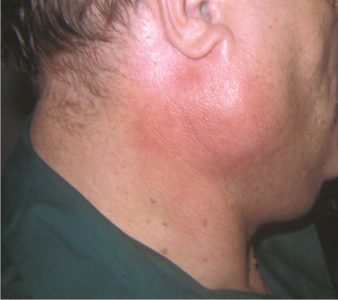
There are 3 paired salivary glands in our body: The parotid gland, the submandibular gland and the sublingual gland.
There are a couple of disorders which can arise from the salivary glands:
- Sialoliths, or salivary stones: this is caused when there is build-up of crystallized saliva deposits in the glands. This leads to a blockage in the glands, causing pain a palpable mass, and surrounding swelling in the area. If the blockage is not cleared, it could also lead to and worsening pain, infection of the gland, and even a small abscess at the site.
- Sialadenitis, or salivary gland infections: When the duct into the mouth is blocked, it can lead to bacterial infections of the salivary gland giving rise to facial swelling, pain on eating or chewing, and if severe abscess.
- Cysts: minor salivary gland or sublingual glands can cause cysts. Sublingual gland cysts are known as a ranula which appear at the floor of mouth. Although non painful by themselves, they can get infected or grow and extend down into the neck.
- Tumours: tumours in the salivary glands can be malignant or benign. Any nodules or masses in the salivary glands need further investigation with scans and a biopsy to decipher their nature.
TREATMENT
Depending upon the diagnosis and the severity of your condition, the treatment can vary. For stones or blockages, treatment options include warm compresses, encouraging saliva flow by consuming sour foods, encouraging hydration. In severe cases, a sialendoscopy and retrieval of stone may be recommended or open surgery to remove affected salivary gland.
In the case of infections, antibiotics and pain relief medication are needed.
Tumours will need to be treated with surgery with or without radiotherapy.