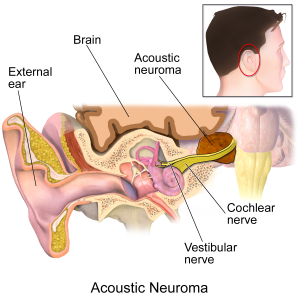
Vestibular Schwannoma, also known as Acoustic Neuroma, is a slow growing tumour arising from the vestibular nerve in the brain. It can be part of a hereditary syndrome known as Neurofibromatosis Type II or can arise de-novo. It can present with:
- Gradual hearing loss
- Sudden hearing loss
- Persistent unilateral tinnitus
- Dizziness
- Facial asymmetry
- Headaches, vomiting and visual disturbances ( in large tumours)
TREATMENT
Treatment for each tumour is tailored according to the extent of the tumour, hearing loss level and patient profile. There is no one size- fits-all solution. In addition, patients with Neurofibromatosis Type II have a treatment strategy for their vestibular schwanommas.
Treatment methods:
- Observation and interval scans
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
- Lateral Skull base Surgery
- Rehabilitation of hearing post-treatment
- VEGFR inhibitors for Neurofibromatosis Type II